Docker has been the de facto containerization ecosystem for more than a decade now. It recently added a model runner that runs many open models locally via a docker model command. In this post, you will learn how to use the Docker model runner to run smoll2 locally and interact with it. Let’s get started! Table of contents # Prerequisites Running Smollm2 with Docker Model Runner Pull a model with Docker model runner Run a model Remove a model Conclusion Prerequisites # Below are some prerequisites you will need installed on the machine you want to run Docker Model Runner (DMR) Docker Model Runner (DMR) is available from Docker Desktop version 4.40 or later, so you will need Docker Desktop version 4.40 or later installed Your hardware will also need to support the functionality, which has GPU backends. I am running the commands shown in this tutorial on a Mac with an Apple Silicon chip If you are running Docker Engine on a Linux distro without Docker Desktop, you will need to install the docker-model-plugin separately with a command like sudo apt-get install docker-model-plugin The easiest way to check if Docker Model Runner (DMR) is available on your machine with Docker Desktop or Docker engine installed is by running: docker model version If you see a version for your Docker Model Runner with the Docker Engine Kind, DMR is available on your machine. In my case, I am running Docker Model Runner version 1.0.6 on Docker Desktop 4.57.0. Given the prerequisites have been mentioned, in the next section, you will run Smollm2 with Docker Model Runner(DMR). Running Smollm2 with Docker Moder Runner # Given that you have tested that you have Docker and Docker Model Runner installed on your system of choice. You will be running the Smollm2(https://huggingface.co/collections/HuggingFaceTB/smollm2) model’s default/latest variant, which is the 360 million parameter one. It is 256.38 MB in size. You might ask why Smollm2. In my opinion, it is small enough to download quickly and does a good job of answering basic questions. If you are not very confident with Docker commands, you can read the Docker for beginners tutorial for a refresher on Docker. You can also read the post on Docker commands like docker pull, docker images, docker run, and others. Pull a model with Docker model runner # You can run the following command to pull Smoll2 from DockerHub: docker model pull ai/smollm2:latest The output will look as follows after Smollm2 open model (by Huggingface) is downloaded to your machine: You can also pull the model from Hugging Face. You can use the Docker Desktop interface to pull the same model after searching in the DockerHub tab, as seen below: But a single command is much easier than following 4 steps on the GUI. Next, to see if the model is pulled (downloaded) correctly, you can run the following command to list all models: docker model list It will show the following output. After that, you can run the Smollm2 35-million-parameter model as discussed next. Run a model # To run the pulled Smollm2 model, you will need to run the following command: docker model run ai/smollm2 "Why is the sky blue? Answer in a single sentence." It will result in something like: The sky is blue because it scatters sunlight in all directions and our eyes are more sensitive to shorter wavelengths of light, like blue and violet. To run the model in an interactive question-answer mode, you can execute the following command: docker model run ai/smollm2 After that, you can chat with the model as follows: To exit the chat, you can type /bye on the command prompt, and it will take you back to your shell/CLI. If you type /?, it will give you more help options as seen below: You can look at all the prompts given to the model on Docker Desktop by clicking the model in the Models screen, which is Smoll2 in this case: Then click the Requests tab: The logs don’t stay for long, though. You can see that the model is responding very fast -- under 6 ms. You can also chat with the model from the Chat tab, as seen below: You can also inspect the mode’s architecture, parameters, and other information in the Inspect tab: The above information is similar to running the docker model inspect smollm2 command. You can find the list of commands supported by docker model in the official Docker documentation. For instance, you can see the running models with docker model ps and try out other commands similar to the main Docker CLI. Smollm2 is an example; at the time of writing, there are 57 models available on Docker Hub. You can pull in Llama, Gemma, Qwen, Kimi, or any other open model of your choice and run it on your machine. The best part is that it is local, fast, and you don’t even need internet to run a model once it is downloaded and running on your local machine. Remove a model # If you want to remove the Smollm2 model, you can run docker model rm smollm2, which will delete the model given an output like: Untagged: index.docker.io/ai/smollm2:latest Deleted: sha256:354bf30d0aa3af413d2aa5ae4f23c66d78980072d1e07a5b0d776e9606a2f0b9 There you go, you pulled a model with Docker Model runner and were able to run it. You had a quick chat with Smollm2. In the next part, you will learn how to connect a model with your own app using Docker Compose. Conclusion # In this quick and useful tutorial, you learned how to pull an open model like Smollm2 from DockerHub and run it on your local machine. This is just scratching the surface, with Docker Model runner you can run many open models on your machine from Gemma to Llama, and from Qwen to Deepseek deepening on your hardware. Keep learning!
Docker has been the de facto containerization ecosystem for more than a decade now. It recently added a model runner that runs many open models locally via a docker model command. In this post, you will learn how to use the Docker model runner to run smoll2 locally and interact with it. Let’s get started!
Table of contents #
Prerequisites #
Below are some prerequisites you will need installed on the machine you want to run Docker Model Runner (DMR)
- Docker Model Runner (DMR) is available from Docker Desktop version 4.40 or later, so you will need Docker Desktop version 4.40 or later installed
- Your hardware will also need to support the functionality, which has GPU backends. I am running the commands shown in this tutorial on a Mac with an Apple Silicon chip
- If you are running Docker Engine on a Linux distro without Docker Desktop, you will need to install the
docker-model-pluginseparately with a command likesudo apt-get install docker-model-plugin
The easiest way to check if Docker Model Runner (DMR) is available on your machine with Docker Desktop or Docker engine installed is by running:
docker model versionIf you see a version for your Docker Model Runner with the Docker Engine Kind, DMR is available on your machine. In my case, I am running Docker Model Runner version 1.0.6 on Docker Desktop 4.57.0.
Given the prerequisites have been mentioned, in the next section, you will run Smollm2 with Docker Model Runner(DMR).
Running Smollm2 with Docker Moder Runner #
Given that you have tested that you have Docker and Docker Model Runner installed on your system of choice. You will be running the Smollm2(https://huggingface.co/collections/HuggingFaceTB/smollm2) model’s default/latest variant, which is the 360 million parameter one. It is 256.38 MB in size. You might ask why Smollm2. In my opinion, it is small enough to download quickly and does a good job of answering basic questions.
If you are not very confident with Docker commands, you can read the Docker for beginners tutorial for a refresher on Docker. You can also read the post on Docker commands like docker pull, docker images, docker run, and others.
Pull a model with Docker model runner #
You can run the following command to pull Smoll2 from DockerHub:
docker model pull ai/smollm2:latestThe output will look as follows after Smollm2 open model (by Huggingface) is downloaded to your machine:
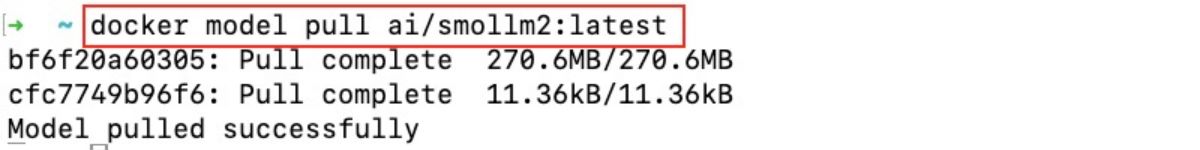
You can also pull the model from Hugging Face.
You can use the Docker Desktop interface to pull the same model after searching in the DockerHub tab, as seen below:
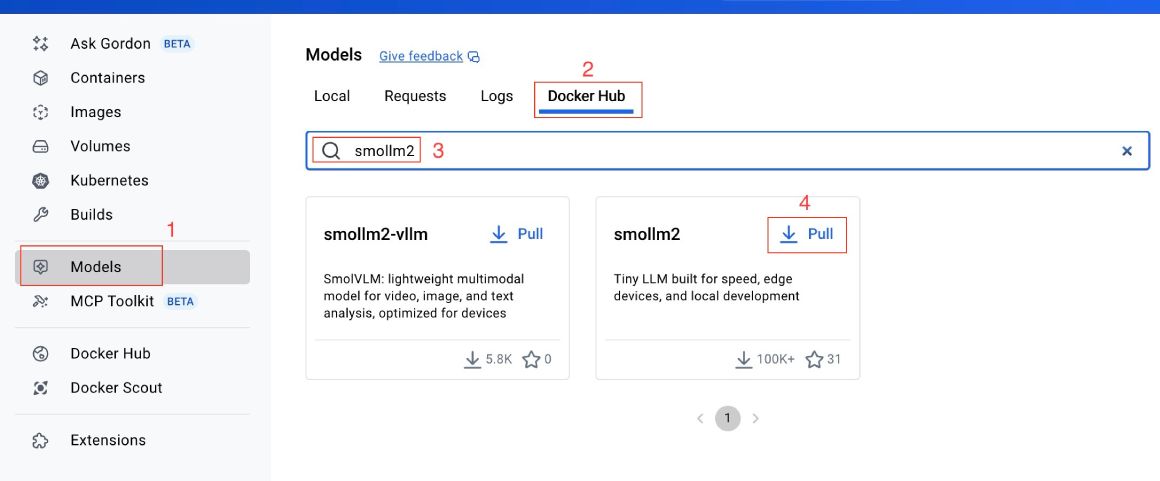
But a single command is much easier than following 4 steps on the GUI. Next, to see if the model is pulled (downloaded) correctly, you can run the following command to list all models:
docker model listIt will show the following output.

After that, you can run the Smollm2 35-million-parameter model as discussed next.
Run a model #
To run the pulled Smollm2 model, you will need to run the following command:
docker model run ai/smollm2 "Why is the sky blue? Answer in a single sentence."It will result in something like:
The sky is blue because it scatters sunlight in all directions and our eyes are more sensitive to shorter wavelengths of light, like blue and violet.
To run the model in an interactive question-answer mode, you can execute the following command:
docker model run ai/smollm2After that, you can chat with the model as follows:

To exit the chat, you can type /bye on the command prompt, and it will take you back to your shell/CLI. If you type /?, it will give you more help options as seen below:

You can look at all the prompts given to the model on Docker Desktop by clicking the model in the Models screen, which is Smoll2 in this case:
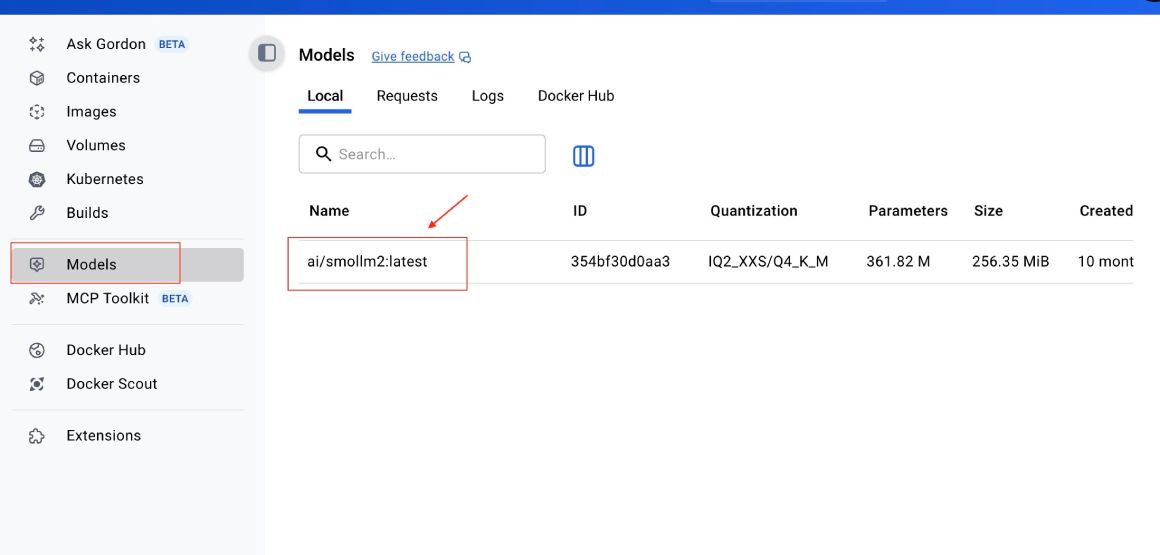
Then click the Requests tab:
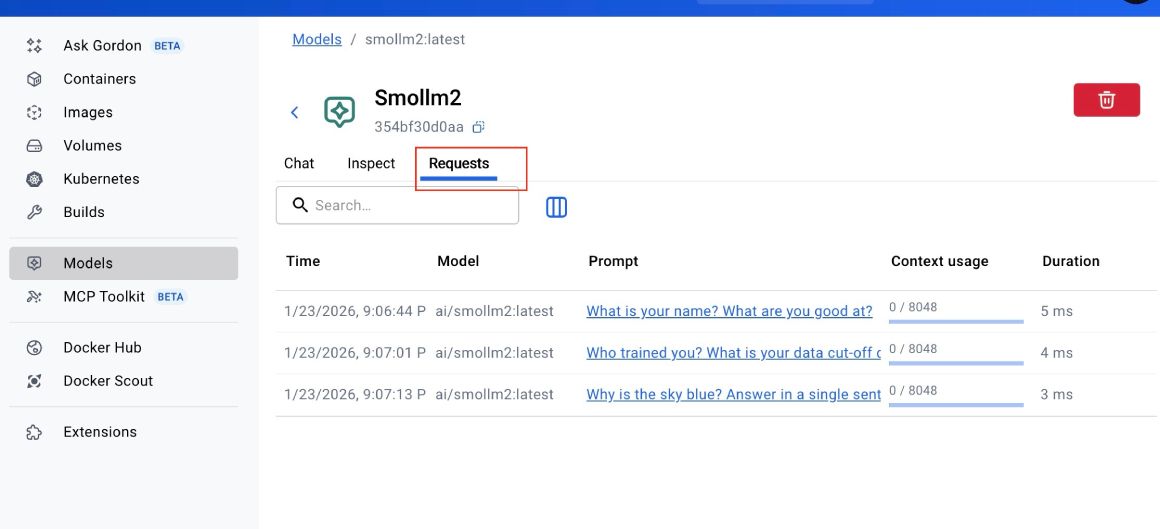
The logs don’t stay for long, though. You can see that the model is responding very fast -- under 6 ms.
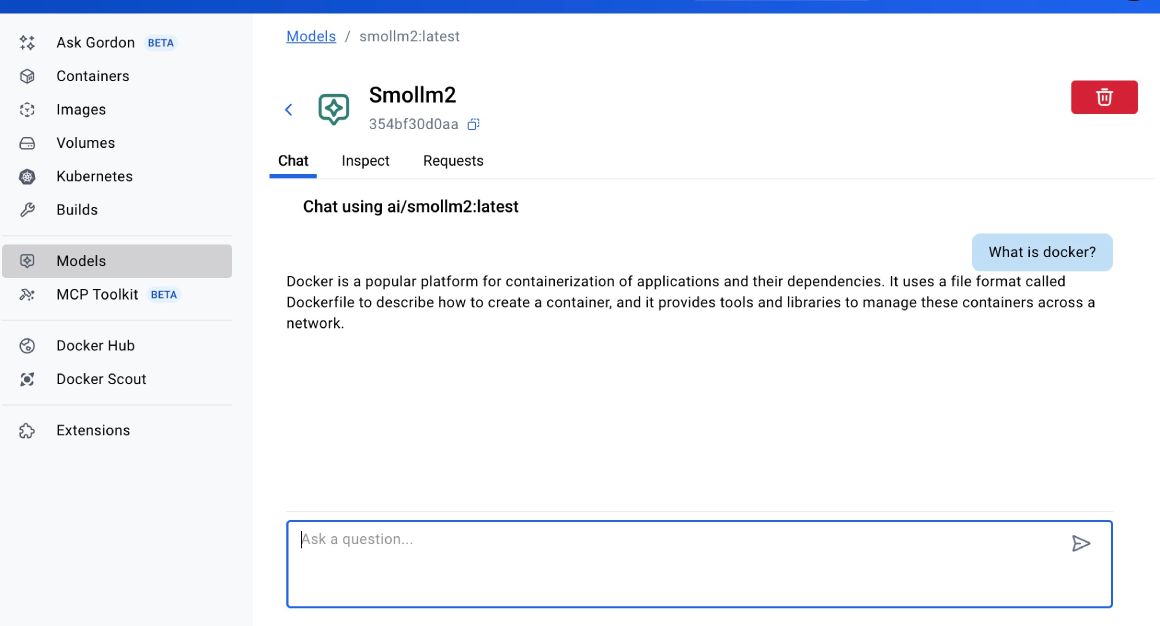
You can also chat with the model from the Chat tab, as seen below:
You can also inspect the mode’s architecture, parameters, and other information in the Inspect tab:
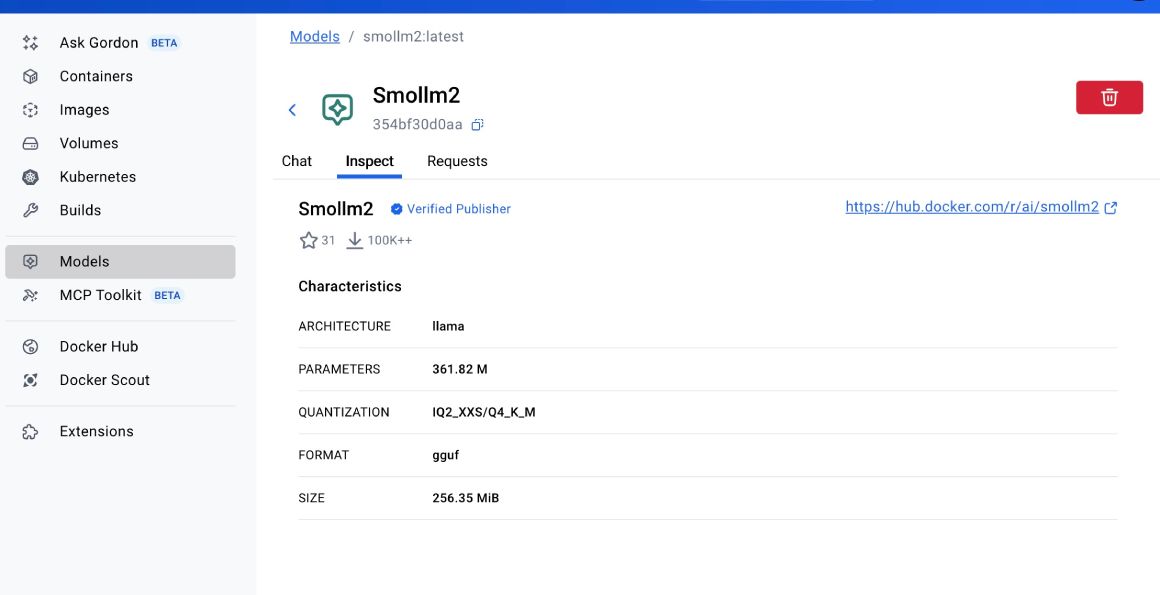
The above information is similar to running the docker model inspect smollm2 command. You can find the list of commands supported by docker model in the official Docker documentation. For instance, you can see the running models with docker model ps and try out other commands similar to the main Docker CLI.
Smollm2 is an example; at the time of writing, there are 57 models available on Docker Hub. You can pull in Llama, Gemma, Qwen, Kimi, or any other open model of your choice and run it on your machine.
The best part is that it is local, fast, and you don’t even need internet to run a model once it is downloaded and running on your local machine.
Remove a model #
If you want to remove the Smollm2 model, you can run docker model rm smollm2, which will delete the model given an output like:
Untagged: index.docker.io/ai/smollm2:latest
Deleted: sha256:354bf30d0aa3af413d2aa5ae4f23c66d78980072d1e07a5b0d776e9606a2f0b9
There you go, you pulled a model with Docker Model runner and were able to run it. You had a quick chat with Smollm2. In the next part, you will learn how to connect a model with your own app using Docker Compose.
Conclusion #
In this quick and useful tutorial, you learned how to pull an open model like Smollm2 from DockerHub and run it on your local machine. This is just scratching the surface, with Docker Model runner you can run many open models on your machine from Gemma to Llama, and from Qwen to Deepseek deepening on your hardware. Keep learning!










![How to use Ollama and Open WebUI with Docker Compose [Part 4]](https://geshan.com.np/images/ollama-docker-compose/01ollama-docker-compose.jpg)


