Adaptive Sync dynamically syncs the monitor's refresh rate to the GPU's frame rate to eliminate screen tearing and reduce game stuttering. The post What is Adaptive Sync? appeared first on ViewSonic Library.
Enter the world of gaming and you will hear the terms refresh rate and frame rate frequently. To make the most of games of all genres, you need hardware that delivers ultra-fast refresh rates and super-high frame rates and understand what Adaptive Sync is.
The short of it: Adaptive Sync prevents screen tearing and game stuttering for the smoothest gameplay possible. Also, make sure to check out ViewSonic gaming monitors with the latest sync capabilities.
However, no matter how advanced the specifications are, monitor refresh rate and graphics card frame rate need to be synced. Without synchronization, gamers experience poor performance, marred with tearing and judder. Companies and organizations such as NVIDIA, AMD, and VESA developed different display technologies that help sync frame rates and refresh rates to eliminate screen tearing and minimize game stuttering. And one such technology is Adaptive Sync.
But first, we should understand what causes screen tearing, game stuttering, and input lag, and how Adaptive Sync resolves them.
What Causes Screen Tearing and Game Stuttering?
Traditional monitors by default refresh their images at a fixed rate. However, when a game requires higher frame rates outside of that fixed rate, especially during fast motion scenes, the monitor might not be able to keep up with that fast increase. The monitor then shows a part of one frame and the next frame at the same time.

As an example, imagine that your game is going at 90 FPS (Frames Per Second), but your monitor’s refresh rate is 60Hz. That means your graphics card is doing 90 updates per second with the display only doing 60. This overlap leads to split images, almost like a tear across the screen. These lines take the beautiful viewing experience away and hamper gameplay.
Game stuttering or micro-stuttering occurs when frames repeat, skip, or freeze. This usually happens when input delay between the GPU and your display happens. Games, especially fast-paced and graphics-intensive types, then feel slow and laggy and players experience input lag and sudden screen hiccups.
Strutter and input lag get big “help” from GPUs that render frames at a slower rate compared to the monitor. A drop in frame rates below your display’s refresh rate leads to game stutter and input delay.
Want to learn more about how your video card affects performance? Esports monitors offer an excellent illustration.
What is V-Sync?
V-Sync, also known as Vertical Sync, is the original GPU technology that synchronizes game frame rates with monitor refresh rates. It was developed primarily to combat screen tearing.
With V-Sync enabled on a monitor, frame rate output remains limited to the maximum refresh rate of that connected monitor. This allows the display to avoid frame rates higher than its refresh rate limit, which eliminates screen tearing. However, if the game’s required framerate drops below the refresh rate of the monitor, having V-Sync enabled causes the FPS to drop even further to match the monitor. This brings added latency, impedes performance, and increases input delay.
To combat this problem, Adaptive Sync was created to clear out screen tearing, reduce lag, and prevent frame stutter.
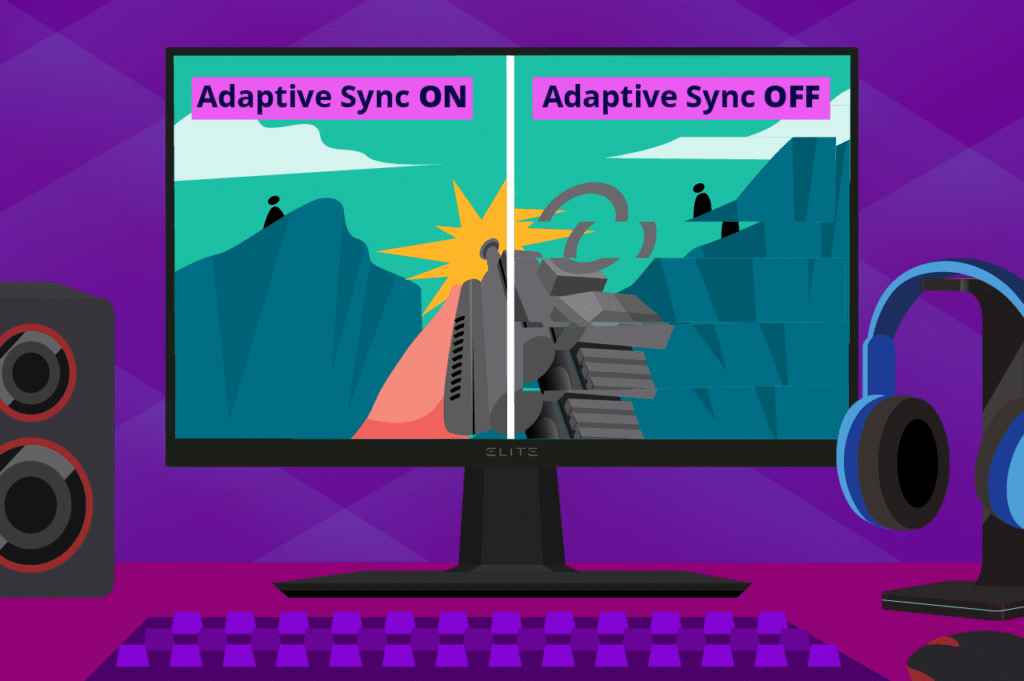
What is Adaptive Sync?
In every game, different scenes demand varying frame rates. The more effects and details the scene has (such as explosions and smoke), the longer it takes to render. Instead of consistently rendering the same frame rate across all scenes, whether they are graphics intensive or not, it makes more sense to sync refresh and frame rate. Good sync means the monitor and GPU work in tandem to adjust monitor refresh rate to frame rate output in real time.
Developed by VESA, Adaptive Sync adjusts display refresh rate to match GPU frame rate output on the fly. Every frame displays as soon as possible to prevent input lag and not repeat. That makes sure in-game stutter and screen tearing do not happen.
Outside of gaming, Adaptive Sync also enables seamless video playback at various frame rates, whether 24 FPS classic movies or 120 FPS streamed content. Adaptive Sync changes monitor refresh rate to match the frame rate of video content to ensure visuals appear smooth and free of interruption.
V-Sync vs. Adaptive Sync: What’s the Difference?
Unlike V-Sync, which caps your GPU frame rate to match your display refresh rate, Adaptive Sync dynamically changes the monitor refresh rate in response to actual frame rate requirements from a game. Adaptive Sync stops screen tearing and addresses the judder that V-Sync causes when FPS drops.

The image above shows the process. Display A waits for Render B to complete before it updates to Display B. This ensures that each frame displays as soon as possible and reduces the possibility of input lag. Frames do not repeat in order to prevent game stutter. The refresh rate adapts to the render frame rate to avoid screen tearing.
AMD FreeSync vs. NVIDIA G-Sync: What’s the Difference?
AMD FreeSync resembles VESA Adaptive Sync. It utilizes VESA’s royalty-free technology to sync refresh rate and frame rate. It also works on most monitors, which keeps prices down. However, AMD has left the frame rate range in the hands of manufacturers, which reduces the usefulness of its sync technology.
NVIDIA G-Sync also uses the same principle as Adaptive Sync. But it relies on proprietary designs that require a license fee and additional work on the part of monitor makers. With NVIDIA supervision, monitors with G-Sync have tighter quality control and therefore slightly higher prices.

The two solutions optimize for respective GPUs. If you own a monitor equipped with G-Sync and want premium features, you should get an NVIDIA graphics card. Likewise, a FreeSync display works best with AMD graphics cards. However, in reality FreeSync and G-Sync have mutual compatibility for baseline performance.
There’s more to learn about the comparison between FreeSync and G-Sync if you’re interested.
Final Thoughts
If you want the smoothest gaming experiences, your monitor needs to support Adaptive Sync. Extra true if you play a lot of fighting or shooting games that require precise reflexes, where even one frame differences lead to victory or defeat. So, make sure to get a display with FreeSync or G-Sync. Real gaming requires it.
Frequently Asked Questions for Adaptive Sync
Adaptive Sync is a display technology feature that allows a monitor’s refresh rate to dynamically match the frame rate output by the GPU (graphics card). In other words, instead of the monitor refreshing at a fixed rate (e.g. 60Hz, 144Hz) regardless of what the GPU sends, Adaptive Sync lets the monitor vary its refresh rate in real time to align with GPU frame output.
When refresh rate and frame rate don’t match, you get visual artifacts like screen tearing (where multiple frames show together) and stutter. Adaptive Sync helps reduce those.
Adaptive Sync eliminates or significantly reduces screen tearing and reduces stutter when frame rates fluctuate. It also reduces unnecessary input lag compared to older sync methods like classic V-Sync (vertical sync). Adaptive Sync improves visual smoothness in gaming, video playback, or anywhere frame rates vary.
– Classic V-Sync (vertical sync) attempts to lock GPU output to monitor refresh rate. The GPU holds back until the monitor is ready. This may lead to added input lag and worse stutter if FPS drops below the refresh rate. Adaptive Sync avoids some of those issues by letting the monitor adjust instead.
– FreeSync by AMD delivers a branded implementation of Adaptive Sync that uses the VESA Adaptive Sync standard with added premium features.
– G-Sync from NVIDIA offers a proprietary technology that also implements variable refresh, often with additional features. Monitors certified G-Sync Compatible build on Adaptive Sync to provide the most consistent GPU to monitor sync.
Adaptive Sync stands as the base standard. FreeSync and G-Sync implement expanded versions of Adaptive Sync to varied degrees of compatibility and performance.
It reduces input lag compared to traditional V-Sync because frames aren’t held back waiting for the monitor’s fixed refresh. There can’t be zero latency due to physics and in some cases, players prefer to use unlocked frame rates (in esports mostly).
No. While games benefit most, video playback, content creation, and general desktop use also benefit from smoother refresh behavior.
Best done before purchase, check monitor specs for Variable Refresh Rate (VRR), Adaptive-Sync, FreeSync, or G-Sync Compatible. If on an existing monitor, check in the GPU driver interface if the option for any of the above is present.
The post What is Adaptive Sync? appeared first on ViewSonic Library.

















